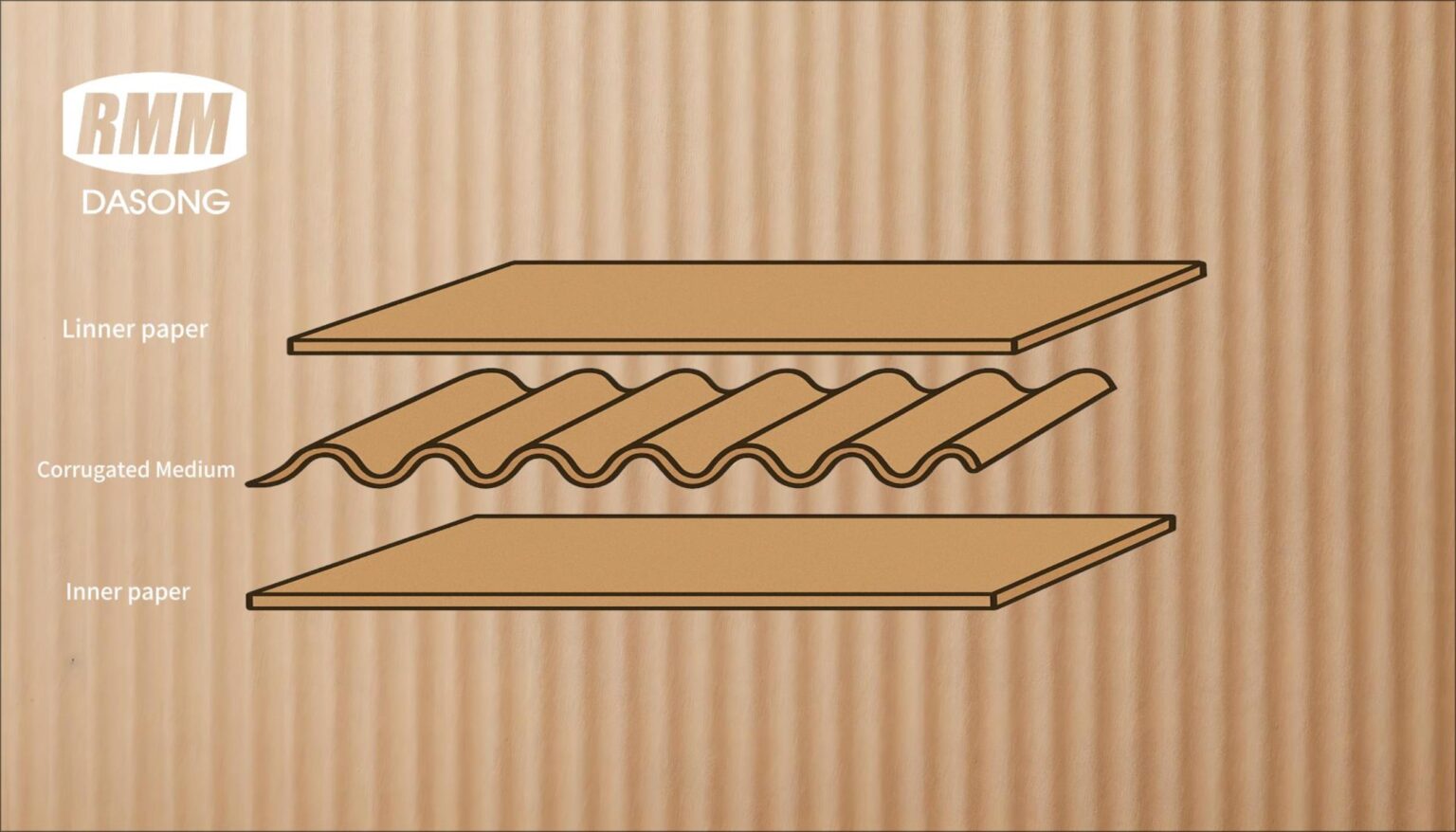
Corrugated cardboard is one of the most widely used packaging materials, valued for its strength, light weight, and versatility. Its performance depends on a simple but well-engineered structure made up of the following key components.
Linerboard
This is the outer layer of the board, typically made of smooth, high-strength kraft paper. It provides a printable surface and the primary compressive strength.
Corrugated Medium
This is the “soul” of corrugated cardboard. Through a special process, paper is pressed into continuous waves (flutes). Though thin and light, this wave structure effectively disperses pressure, offering excellent cushioning and impact resistance.
Different flute types (A, B, C, E, F, etc.) are used to balance strength, thickness, and material efficiency.
Adhesive
Starch-based adhesives bond the linerboard to the corrugated medium, ensuring structural integrity and long-term stability of the board.
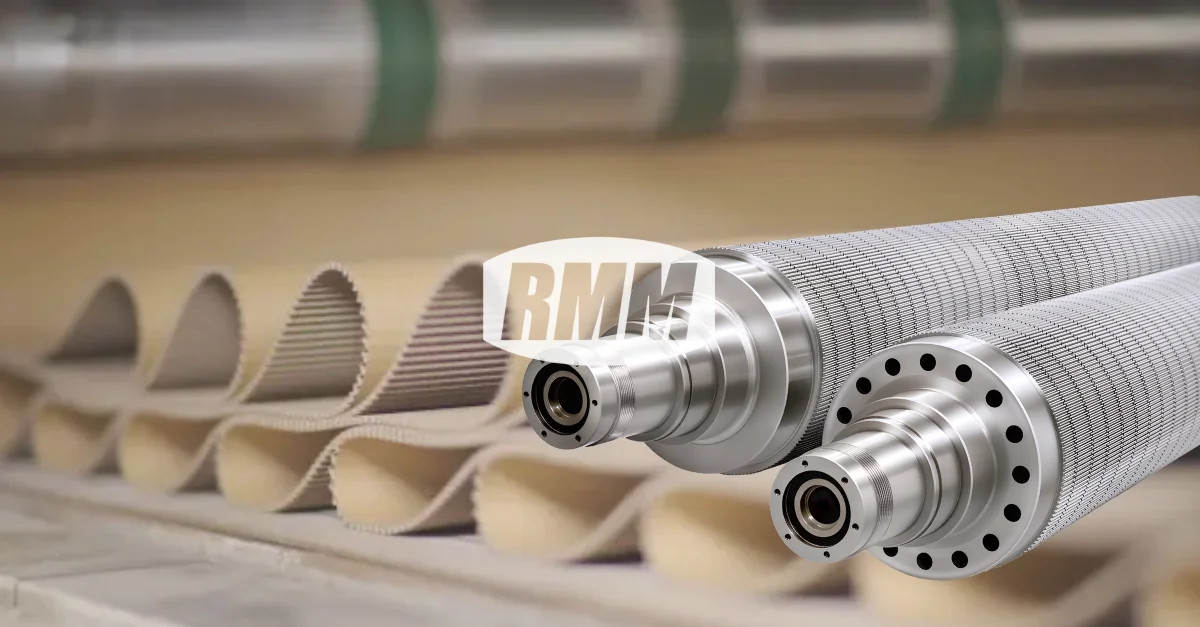
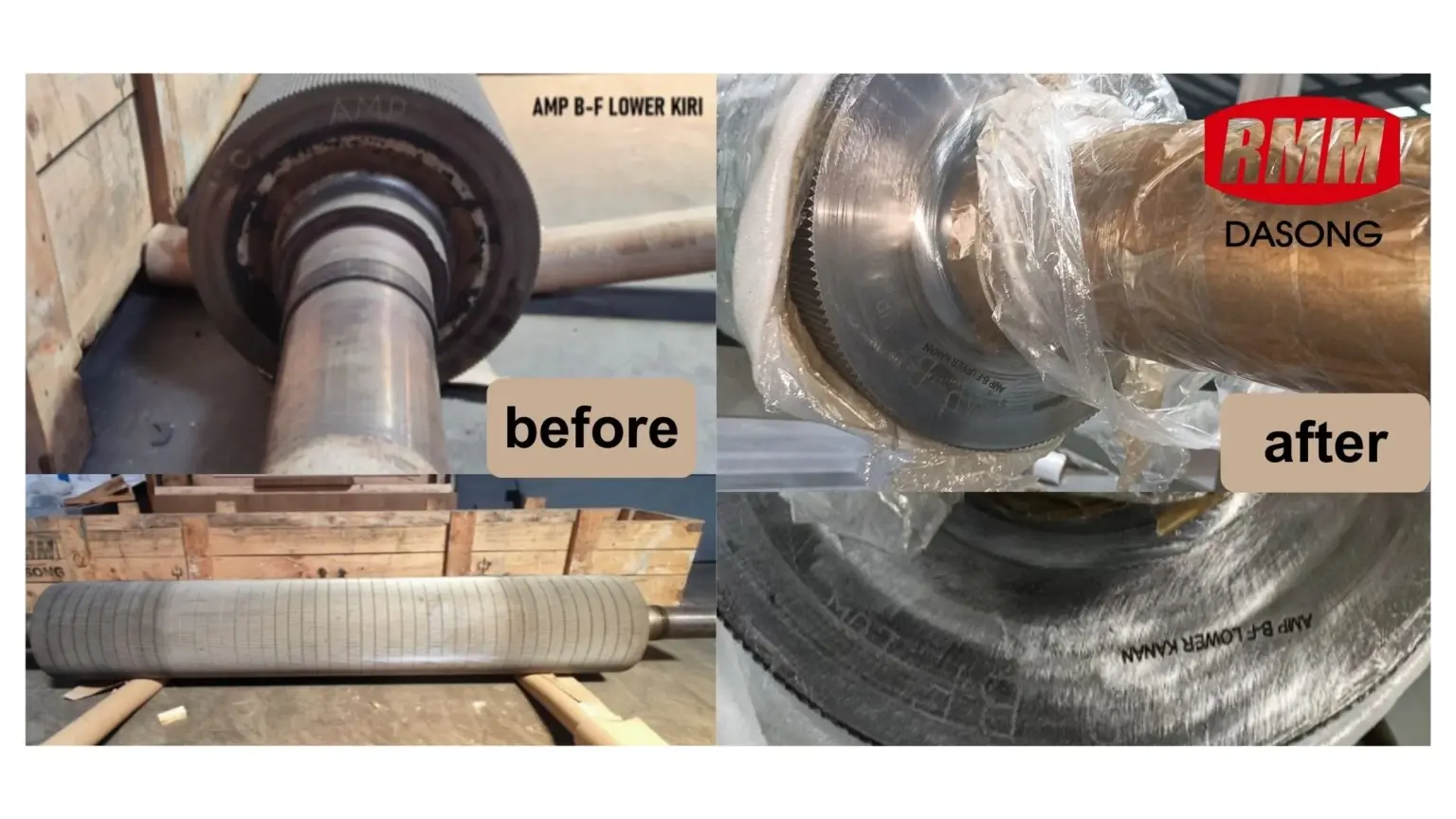
The Role of Corrugating Rolls in Corrugated Cardboard
Corrugating rolls are the core forming components in corrugated board production.
They shape the corrugated medium into precise flute profiles under controlled heat and pressure.
High-quality corrugating rolls ensure:
- Accurate flute shape and height
- Consistent bonding between medium and liner
- Stable board thickness and strength
In short, while corrugated cardboard appears simple, its quality is largely determined by the precision and performance of the corrugating rolls that form its structure.